Running and Compiling HalideOS on your System #
Running HalideOS in Oracle Virtual Box #
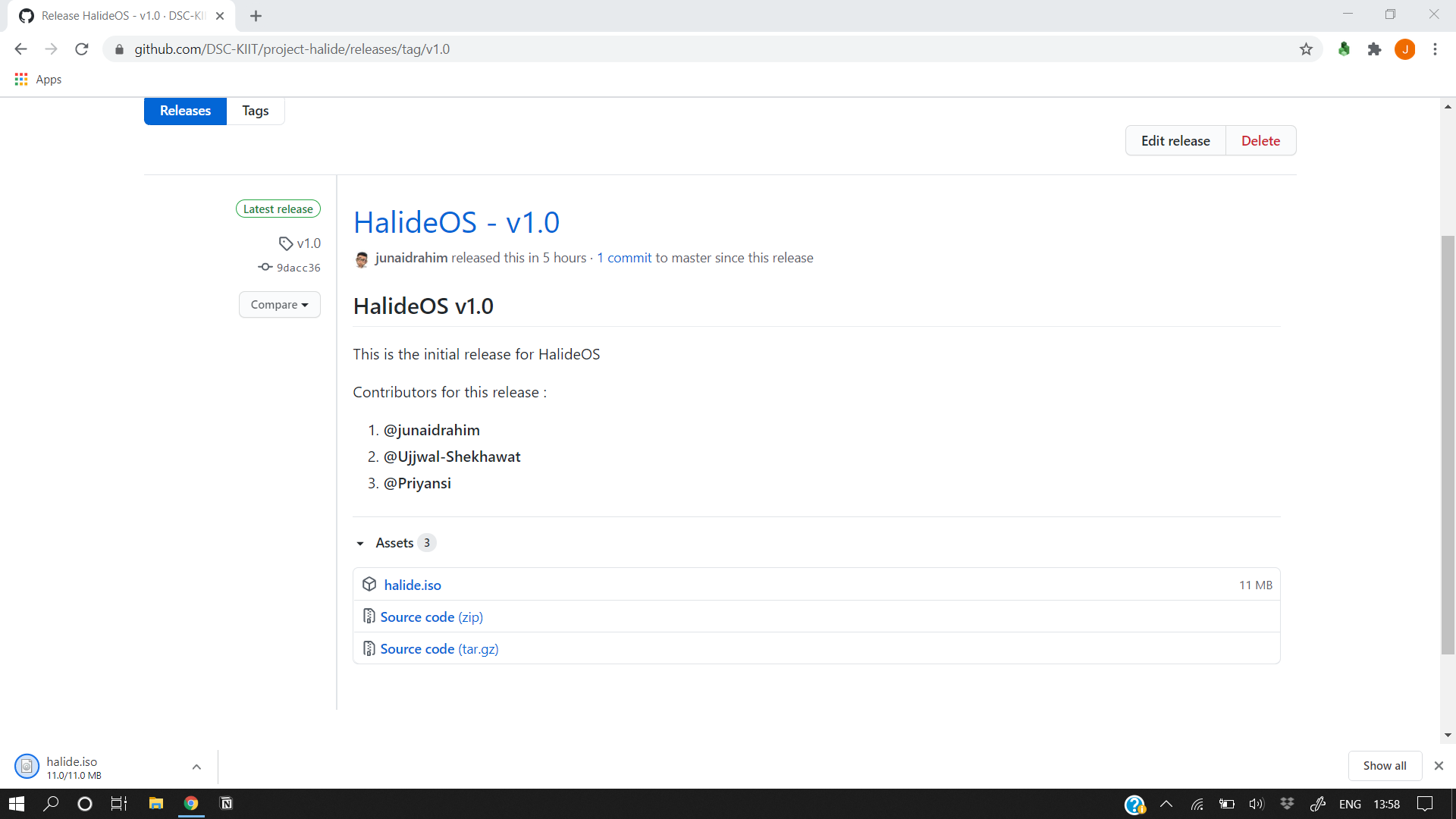
- Head over to the
Releases section of the GitHub repository and download the
halide.isofile.
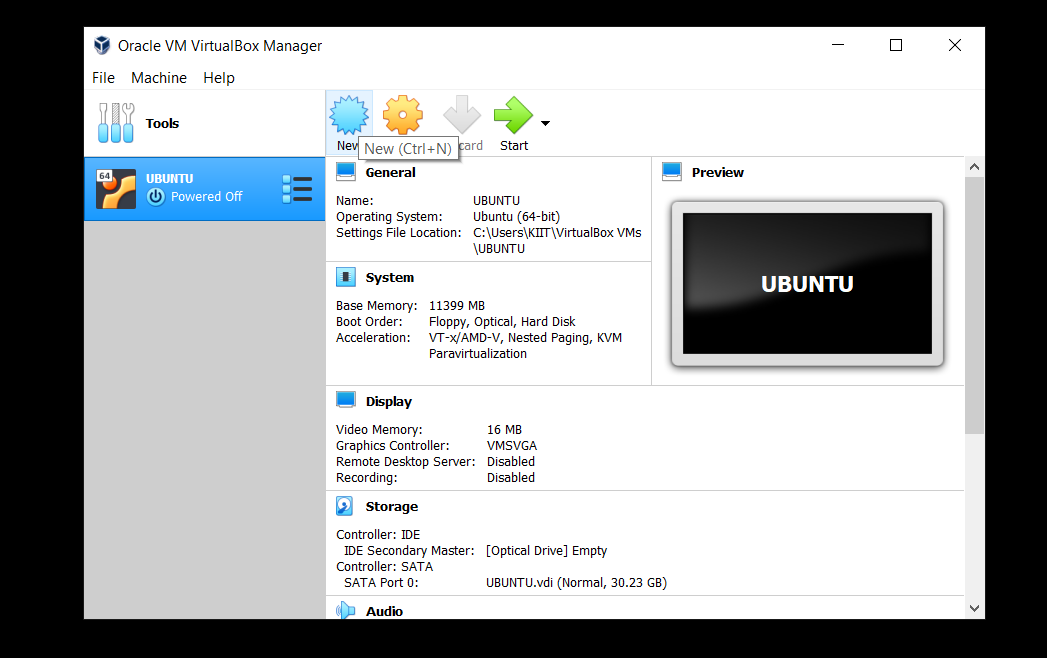
- Open up Oracle VM VirtualBox. Click on New.
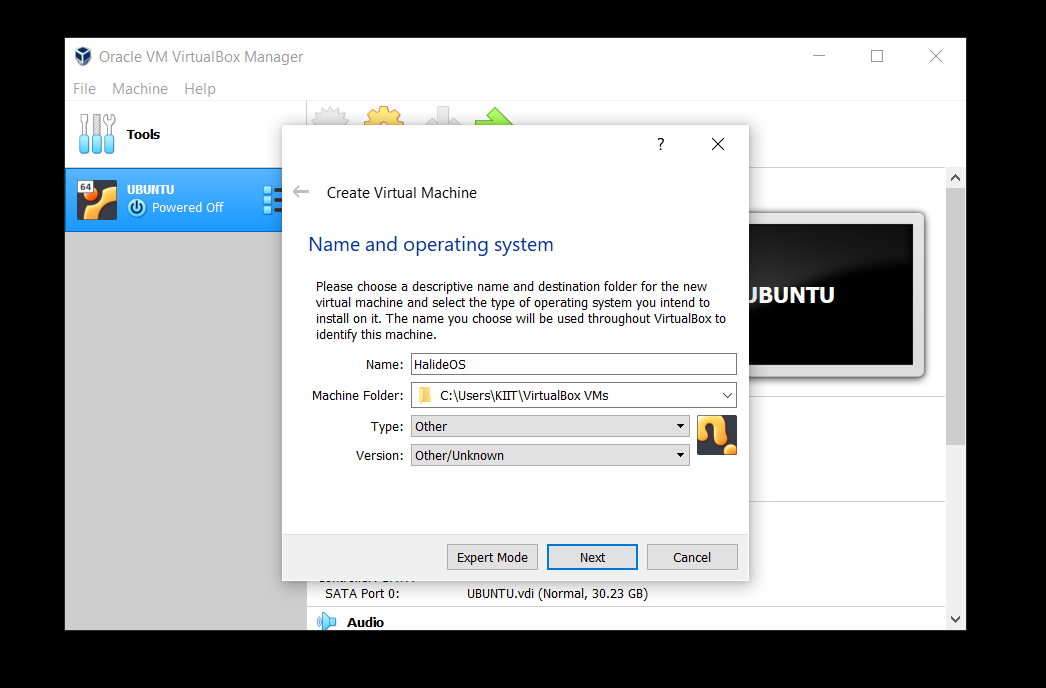
- Put HalideOS as the name. Set Type to Other and Version to Other/Unknown.
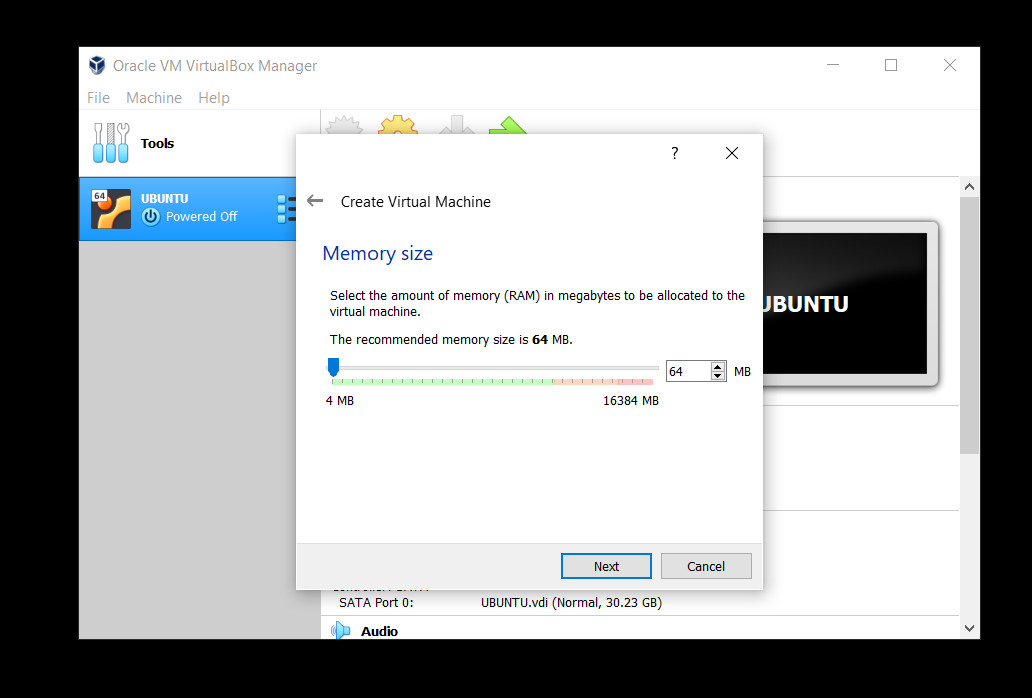
- Set the memory size. 64 MB will be enough.
- Click on Next and select Do not add a virtual disk and click on Create.
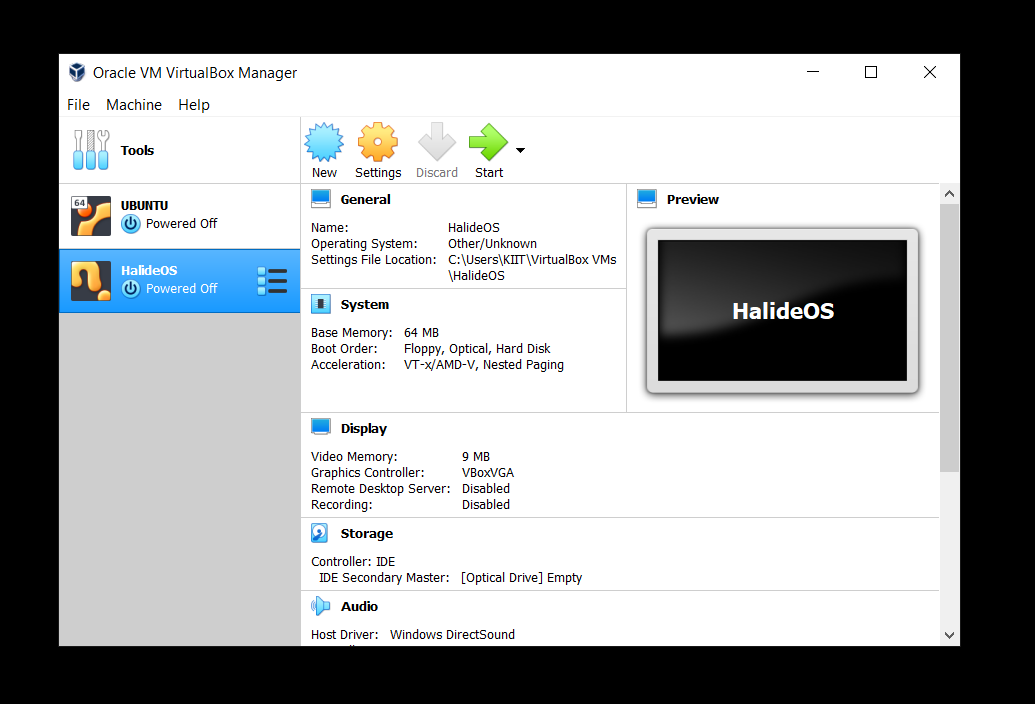
- You will see an instance created. Now we need to load the
halide.isofile we just downloaded. For that, navigate to Settings.
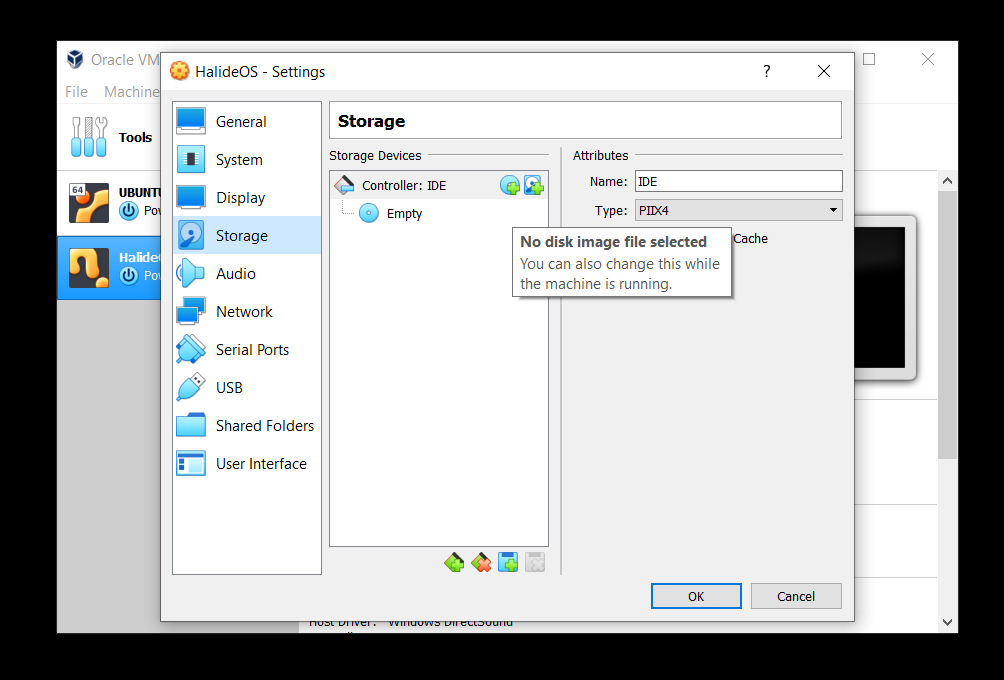
- Under Settings, go to Storage and click on the Empty option in the left pane.
- Click the CD like icon next to IDE Secondary Master.
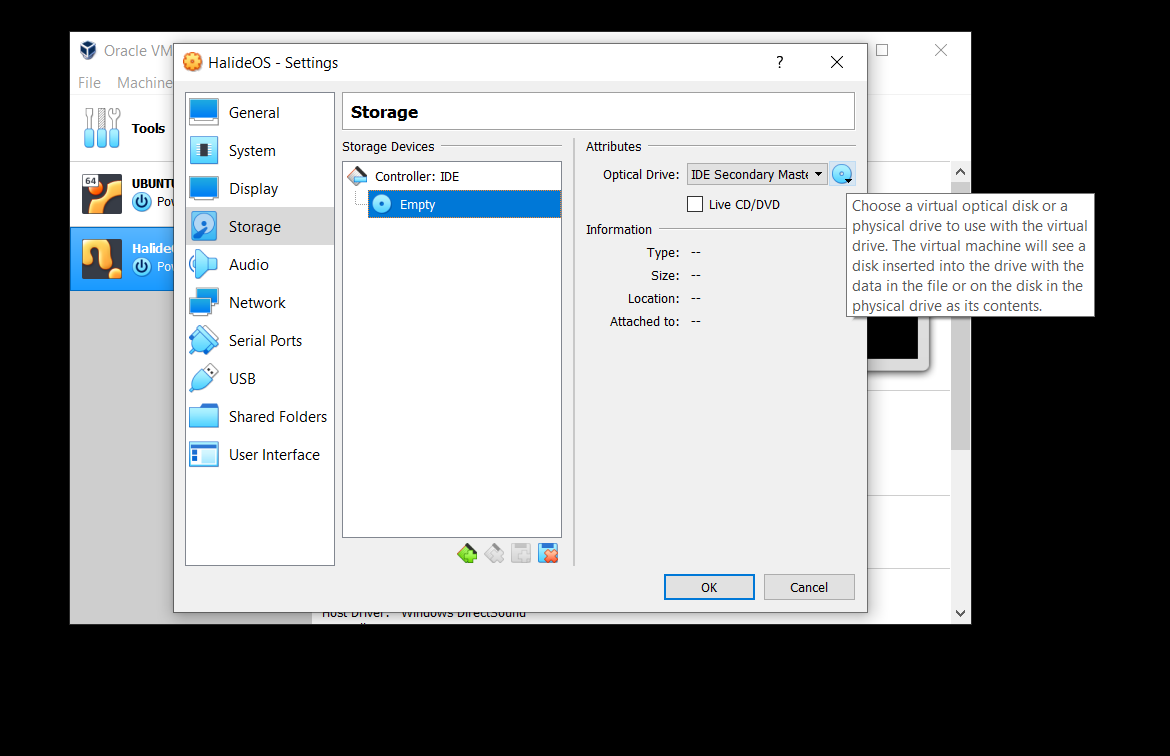
- Choose the
halide.isofile.
- Then click OK.
- You are all set, just click on Start to fire up HalideOS.
- Put your name as the username. Password is
dsc-kiit
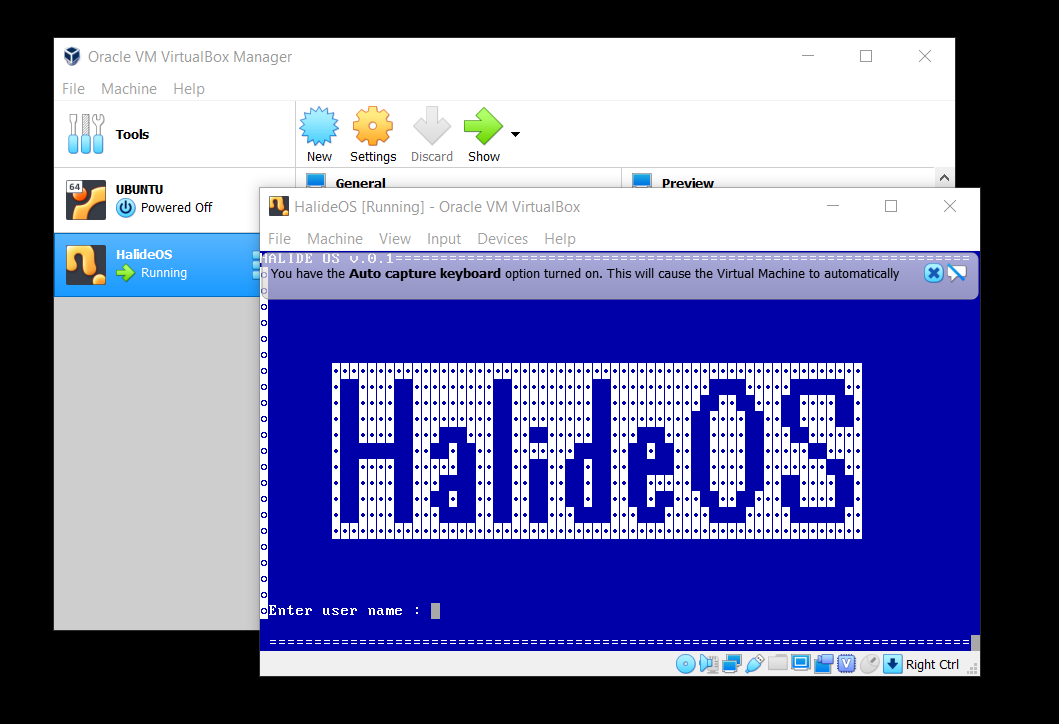
- Press Enter
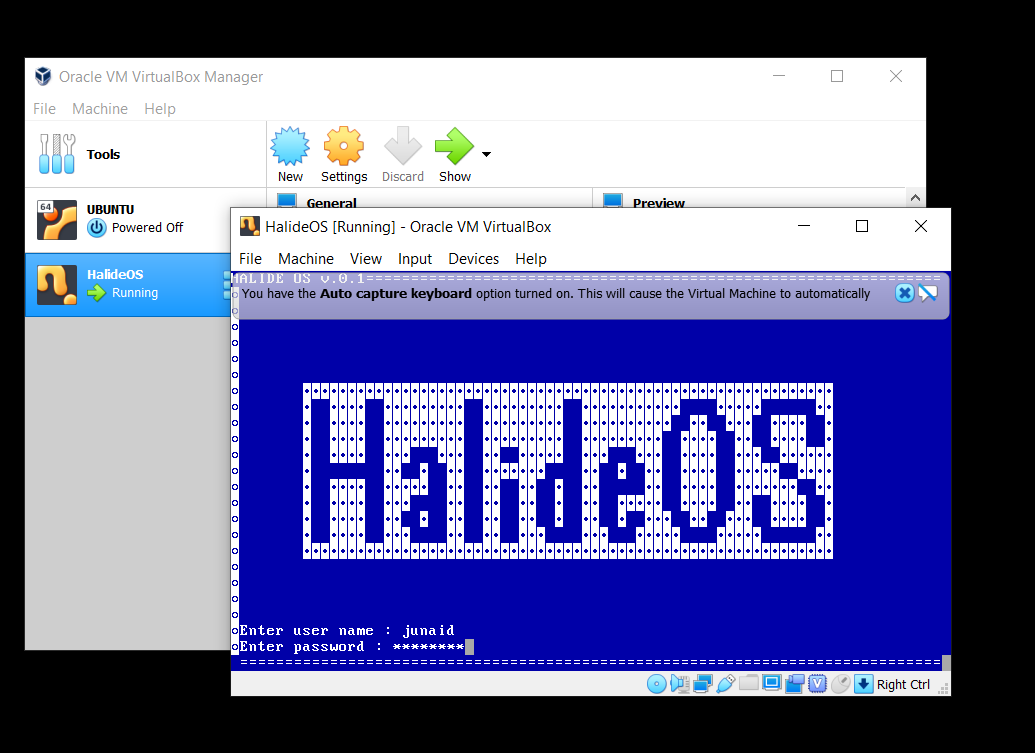
- You will be logged in and a console will be setup for you
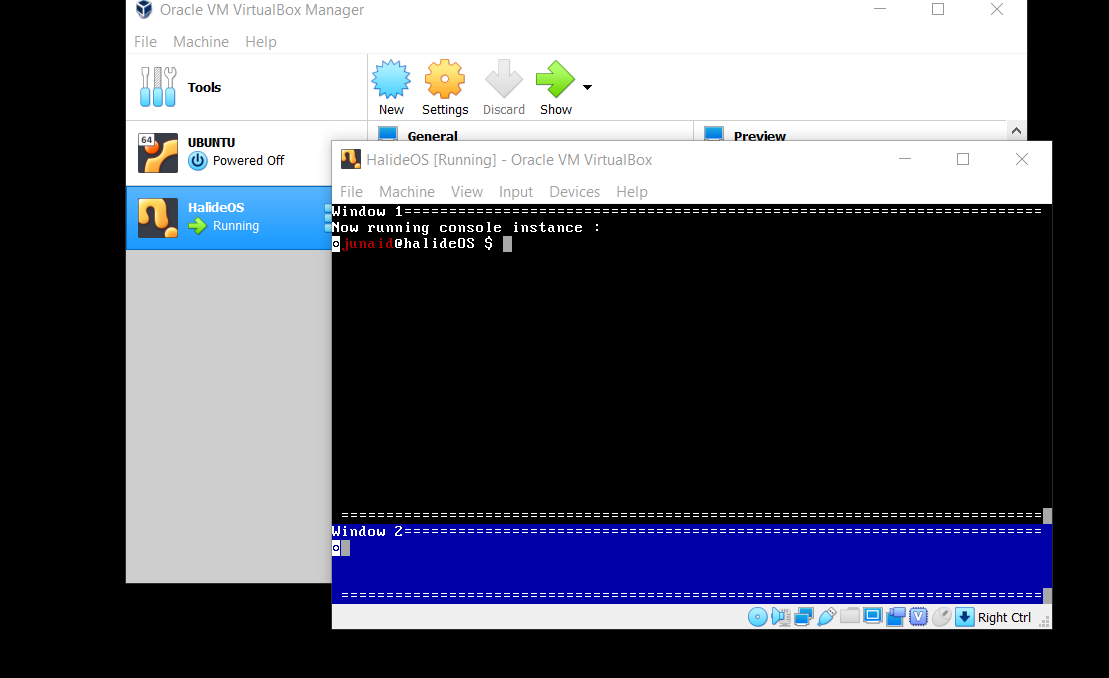
Congratulations, you just booted into HalideOS!
Commands #
These are the commands that are available in the HalideOS console:
about- Know more about HalideOShelp- Get a list of all available commandscalculator- A basic calculator that can evaluate expressions like10-3*2(don’t put spaces or brackets)greet- Get a greetingclear- Clears the consoleswitch window- Switches to the next window
Try them out for yourself.
If you’re curious then the source code for halide is available at https://github.com/DSC-KIIT/project-halide
Compiling HalideOS from Source #
This section will help you with setting up your development environment so that you can compile the code for HalideOS yourself and run it in an emulator. This is a good place to start if you are intersted in contributing code to the project.
Dependencies #
It is recommended that you used a Linux based operating system for building HalideOS. The C/C++ development tools and the entire ecosystem is much easier to use on a Linux based system.
g++- A C++ compilernasmoras- An x86 assemblerld- The GNU Linkermake- GNU Make, a build tool for Linuxqemu- An x86 Emulatorgit- For version control- A text editor of your choice. We use Visual Studio Code
You can Google up how to install these tools for your host operating system. On Linux based systems you will mostly install them using your package manager.
Once you have all these set up on your machine, run the following commands
git clone https://github.com/DSC-KIIT/project-halide
cd project-halide/src
make run
This will compile and build kernel.iso in the src/ directory and start it in qemu.
You can run make help to get a list of all the commands available for various stages of compilation.
Please refer to the Documentation section of the website for more details on the design and the code.